- Zimbabwe
-
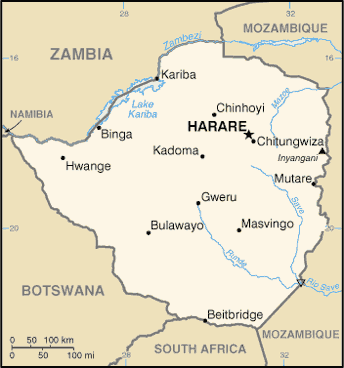 Introduction ::ZimbabweBackground:The UK annexed Southern Rhodesia from the [British] South Africa Company in 1923. A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. In 1965 the government unilaterally declared its independence, but the UK did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country (then called Rhodesia). UN sanctions and a guerrilla uprising finally led to free elections in 1979 and independence (as Zimbabwe) in 1980. Robert MUGABE, the nation's first prime minister, has been the country's only ruler (as president since 1987) and has dominated the country's political system since independence. His chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. Ignoring international condemnation, MUGABE rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his reelection. In April 2005, the capital city of Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. President MUGABE in June 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months. General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with the opposition winning a majority of seats in parliament. MDC opposition leader Morgan TSVANGIRAI won the most votes in the presidential polls, but not enough to win outright. In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of TSVANGIRAI from the ballot. Extensive evidence of violence and intimidation resulted in international condemnation of the process. Difficult negotiations over a power-sharing government, in which MUGABE remained president and TSVANGIRAI became prime minister, were finally settled in February 2009, although the leaders failed to agree upon many key outstanding governmental issues. MUGABE was reelected president in June 2013 in balloting that was severely flawed and internationally condemned.Geography ::ZimbabweLocation:Southern Africa, between South Africa and ZambiaGeographic coordinates:20 00 S, 30 00 EArea:total: 390,757 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 61land: 386,847 sq kmwater: 3,910 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than MontanaLand boundaries:total: 3,066 kmborder countries: Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:tropical; moderated by altitude; rainy season (November to March)Terrain:mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld); mountains in eastElevation extremes:lowest point: junction of the Runde and Save Rivers 162 mhighest point: Inyangani 2,592 mNatural resources:coal, chromium ore, asbestos, gold, nickel, copper, iron ore, vanadium, lithium, tin, platinum group metalsLand use:arable land: 10.49%permanent crops: 0.31%other: 89.2% (2011)Irrigated land:1,735 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:20 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.21 cu km/yr (14%/7%/79%)per capita: 333.5 cu m/yr (2002)Natural hazards:recurring droughts; floods and severe storms are rareEnvironment - current issues:deforestation; soil erosion; land degradation; air and water pollution; the black rhinoceros herd - once the largest concentration of the species in the world - has been significantly reduced by poaching; poor mining practices have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollutionEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protectionsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural riverine boundary with Zambia; in full flood (February-April) the massive Victoria Falls on the river forms the world's largest curtain of falling water; Lake Kariba on the Zambia-Zimbabwe border forms the world's largest reservoir by volume (180 cu km; 43 cu mi)People and Society ::ZimbabweNationality:noun: Zimbabwean(s)adjective: ZimbabweanEthnic groups:African 98% (Shona 82%, Ndebele 14%, other 2%), mixed and Asian 1%, white less than 1%Languages:English (official), Shona, Sindebele (the language of the Ndebele, sometimes called Ndebele), numerous but minor tribal dialectsReligions:syncretic (part Christian, part indigenous beliefs) 50%, Christian 25%, indigenous beliefs 24%, Muslim and other 1%Population:13,182,908 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 72note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 39.4% (male 2,623,606/female 2,570,028)15-24 years: 22.5% (male 1,472,186/female 1,493,816)25-54 years: 30.8% (male 2,039,943/female 2,018,589)55-64 years: 3.7% (male 176,951/female 311,113)65 years and over: 3.6% (male 193,147/female 283,529) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 76.4 %youth dependency ratio: 69.6 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.8 %potential support ratio: 14.7 (2013)Median age:total: 19.5 yearsmale: 19 yearsfemale: 20 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:4.38% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Birth rate:32.41 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Death rate:11.4 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Net migration rate:22.76 migrant(s)/1,000 populationcountry comparison to the world: 3note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2013 est.)Urbanization:urban population: 38.6% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:HARARE (capital) 1.606 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.95 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.95 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.57 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.7 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:20.5note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011 est.)Maternal mortality rate:570 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 15Infant mortality rate:total: 27.25 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 71male: 29.63 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 24.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 53.86 yearscountry comparison to the world: 209male: 53.79 yearsfemale: 53.93 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:3.58 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 45Contraceptive prevalence rate:58.5% (2010/11)Physicians density:0.16 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:1.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 98% of populationrural: 69% of populationtotal: 80% of populationunimproved:urban: 2% of populationrural: 31% of populationtotal: 20% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 52% of populationrural: 32% of populationtotal: 40% of populationunimproved:urban: 48% of populationrural: 68% of populationtotal: 60% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:14.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1.2 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 9HIV/AIDS - deaths:83,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 143Children under the age of 5 years underweight:10.1% (2011)country comparison to the world: 68Education expenditures:2.5% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 158Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and write Englishtotal population: 83.6%male: 87.8%female: 80.1% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 9 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 9 years (2003)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 7.6%country comparison to the world: 123male: 7.6%female: 7.6% (2004)Government ::ZimbabweCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Zimbabweconventional short form: Zimbabweformer: Southern Rhodesia, RhodesiaGovernment type:parliamentary democracyCapital:name: Hararegeographic coordinates: 17 49 S, 31 02 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:8 provinces and 2 cities* with provincial status; Bulawayo*, Harare*, Manicaland, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland East, Mashonaland West, Masvingo, Matabeleland North, Matabeleland South, MidlandsIndependence:18 April 1980 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 18 April (1980)Constitution:21 December 1979Legal system:mixed legal system of English common law, Roman-Dutch civil law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987); Vice President Joice MUJURU (since 6 December 2004) and Vice President John Landa NKOMO (since December 2009)head of government: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987) note - according to the new constitution, following the 31 July 2013 presidential elections the position of Prime Minister was abolishedcabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president; responsible to the House of Assembly(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: presidential candidates nominated with a nomination paper signed by at least 10 registered voters (at least one from each province) and elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); elections last held on 31 July 2013 (next to be held in 2018); co-vice presidents drawn from party leadershipelection results: Robert Gabriel MUGABE reelected president; percent of vote - Robert Gabriel MUGABE 61.1%, Morgan TSVANGIRAI 34.4%, Welshman NCUBE 2.7% other 1.8%; note - the election process was considered flawed and roundly criticised by election monitors and international bodiesLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of a Senate (93 seats - 60 members elected by popular vote for a five-year term, 10 provincial governors nominated by the president, 16 traditional chiefs elected by the Council of Chiefs, 2 seats held by the president and deputy president of the Council of Chiefs, and 5 members appointed by the president) and a House of Assembly (210 seats - members elected by popular vote for five-year terms)elections: last held on 31 July 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ZANU-PF 37 MDC 23; House of Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ZANU-PF 160, MDC 49, other 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 4 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president upon recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body consisting of the chief justice, Public Service Commission chairman, attorney general, and 2-3 members appointed by the president; judges normally serve until age 65, but can elect to serve until age 70subordinate courts: High Court, regional magistrate courts, and special courtsPolitical parties and leaders:African National Party or ANP [Egypt DZINEMUNHENZVA]Movement for Democratic Change - Tsvangirai or MDC-T [Morgan TSVANGIRAI]Movement for Democratic Change - Ncube or MDC-N [Welshman NCUBE]Peace Action is Freedom for All or PAFAUnited Parties [Abel MUZOREWA]United People's Party or UPP [Daniel SHUMBA]Zimbabwe African National Union-Ndonga or ZANU-Ndonga [Wilson KUMBULA]Zimbabwe African National Union-Patriotic Front or ZANU-PF [Robert Gabriel MUGABE]Zimbabwe African Peoples Union or ZAPU [Dumiso DABENGWA]Zimbabwe Youth in Alliance or ZIYAPolitical pressure groups and leaders:Crisis in Zimbabwe CoalitionNational Constitutional Assembly or NCA [Lovemore MADHUKU]Women of Zimbabwe Arise or WOZA [Jenny WILLIAMS]Zimbabwe Congress of Trade Unions or ZCTU [Wellington CHIBEBE]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Machivenyika MAPURANGAchancery: 1608 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 332-7100FAX: [1] (202) 483-9326Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador David Bruce WHARTONembassy: 172 Herbert Chitepo Avenue, Hararemailing address: P. O. Box 3340, Hararetelephone: [263] (4) 250-593 through 250-594FAX: [263] (4) 796-488, or 722-618Flag description:seven equal horizontal bands of green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow, and green with a white isosceles triangle edged in black with its base on the hoist side; a yellow Zimbabwe bird representing the long history of the country is superimposed on a red five-pointed star in the center of the triangle, which symbolizes peace; green represents agriculture, yellow mineral wealth, red the blood shed to achieve independence, and black stands for the native peopleNational symbol(s):Zimbabwe bird symbol; African fish eagleNational anthem:name: ""Kalibusiswe Ilizwe leZimbabwe"" [Northern Ndebele language] ""Simudzai Mureza WeZimbabwe"" [Shona] (Blessed Be the Land of Zimbabwe)lyrics/music: Solomon MUTSWAIRO/Fred Lecture CHANGUNDEGAnote: adopted 1994Economy ::ZimbabweEconomy - overview:Zimbabwe's economy is growing despite continuing political uncertainty. Following a decade of contraction from 1998 to 2008, Zimbabwe's economy recorded real growth of more than 9% per year in 2010-11, before slowing to 5% in 2012, due in part to a poor harvest and low diamond revenues. However, the government of Zimbabwe still faces a number of difficult economic problems, including infrastructure and regulatory deficiencies, ongoing indigenization pressure, policy uncertainty, a large external debt burden, and insufficient formal employment. Zimbabwe''s 1998-2002 involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government''s subsequent land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products. Until early 2009, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely printed money to fund the budget deficit, causing hyperinflation. Dollarization in early 2009 - which allowed currencies such as the Botswana pula, the South Africa rand, and the US dollar to be used locally - ended hyperinflation and reduced inflation to about 10%, but exposed structural weaknesses that continue to inhibit broad-based growth.GDP (purchasing power parity):$7.366 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 159$7.054 billion (2011 est.)$6.38 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$9.802 billionnote: in 2009, the Zimbabwean dollar was taken out of circulation, making Zimbabwe's GDP at the official exchange rate a highly inaccurate statistic (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7310.6% (2011 est.)9.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 227$500 (2011 est.)$500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 68%government consumption: 29.4%investment in fixed capital: 21.9%exports of goods and services: 67.9%imports of goods and services: -87.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 20.3%industry: 25.1%services: 54.6% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, cotton, tobacco, wheat, coffee, sugarcane, peanuts; sheep, goats, pigsIndustries:mining (coal, gold, platinum, copper, nickel, tin, diamonds, clay, numerous metallic and nonmetallic ores), steel; wood products, cement, chemicals, fertilizer, clothing and footwear, foodstuffs, beveragesIndustrial production growth rate:4.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Labor force:3.931 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 66%industry: 10%services: 24% (1996)Unemployment rate:95% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20280% (2005 est.)note: figures reflect underemployment; true unemployment is unknown and, under current economic conditions, unknowablePopulation below poverty line:68% (2004)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2%highest 10%: 40.4% (1995)Distribution of family income - Gini index:50.1 (2006)country comparison to the world: 2350.1 (1995)Budget:revenues: $NAexpenditures: $NATaxes and other revenues:NA% of GDPBudget surplus (+) or deficit (-):NA% of GDPPublic debt:187.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2180.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):8.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1845.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:7.17% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1975% (31 December 2007)Commercial bank prime lending rate:30% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 534% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$12.27 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 74$6.586 billion (31 December 2011 est.)note: Zimbabwe's central bank no longer publishes data on monetary aggregates, except for bank deposits, which amounted to $2.1 billion in November 2010; the Zimbabwe dollar stopped circulating in early 2009; since then, the US dollar and South African rand have been the most frequently used currencies; there are no reliable estimates of the amount of foreign currency circulating in ZimbabweStock of broad money:$11 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 104$22.71 billion (31 December 2012 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$9.844 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 99$6.289 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$10.9 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 70$11.48 billion (31 December 2010)$3.83 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:-$521.9 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 96-$621.5 million (2011 est.)Exports:$3.314 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127$2.932 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:platinum, cotton, tobacco, gold, ferroalloys, textiles/clothingExports - partners:China 20.4%, South Africa 14.9%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 12.9%, Botswana 11.5%, Italy 4.4% (2012)Imports:$4.569 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 132$4.272 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, other manufactures, chemicals, fuels, food productsImports - partners:South Africa 51.2%, China 9.7% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$575.6 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 147$660.3 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$8.767 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 102$6.276 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Zimbabwean dollars (ZWD) per US dollar -234.25 (2010)234.25 (2009)9,686.8 (2007)note: the dollar was adopted as a legal currency in 2009; since then the Zimbabwean dollar has experienced hyperinflation and is essentially worthlessEnergy ::ZimbabweElectricity - production:7.615 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Electricity - consumption:12.54 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Electricity - exports:53 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - imports:5.497 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.005 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Electricity - from fossil fuels:66.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:33.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Refined petroleum products - consumption:19,030 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Refined petroleum products - imports:13,140 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 124Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:8.493 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Communications ::ZimbabweTelephones - main lines in use:356,000 (2011)country comparison to the world: 109Telephones - mobile cellular:9.2 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 81Telephone system:general assessment: system was once one of the best in Africa, but now suffers from poor maintenancedomestic: consists of microwave radio relay links, open-wire lines, radiotelephone communication stations, fixed wireless local loop installations, and a substantial mobile-cellular network; Internet connection is available in Harare and planned for all major towns and for some of the smaller onesinternational: country code - 263; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat; 2 international digital gateway exchanges (in Harare and Gweru) (2010)Broadcast media:government owns all local radio and TV stations; foreign shortwave broadcasts and satellite TV are available to those who can afford antennas and receivers; in rural areas, access to TV broadcasts is extremely limited (2007)Internet country code:.zwInternet hosts:30,615 (2012)country comparison to the world: 108Internet users:1.423 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 84Transportation ::ZimbabweAirports:196 (2013)country comparison to the world: 29Airports - with paved runways:total: 17over 3,047 m: 32,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1791,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 104under 914 m:72 (2013)Pipelines:refined products 270 km (2013)Railways:total: 3,427 kmcountry comparison to the world: 50narrow gauge: 3,427 km 1.067-m gauge (313 km electrified) (2008)Roadways:total: 97,267 kmcountry comparison to the world: 45paved: 18,481 kmunpaved: 78,786 km (2002)Waterways:(some navigation possible on Lake Kariba) (2011)Ports and terminals:Binga, KaribaMilitary ::ZimbabweMilitary branches:Zimbabwe Defense Forces (ZDF): Zimbabwe National Army (ZNA), Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-24 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women are eligible to serve (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,616,051females age 16-49: 2,868,376 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,528,166females age 16-49: 1,646,041 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 154,870female: 152,550 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:3.8% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 26Transnational Issues ::ZimbabweDisputes - international:Namibia has supported, and in 2004 Zimbabwe dropped objections to, plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river; South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: undetermined (political violence, human rights violations, land reform, and economic collapse) (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Zimbabwe is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Zimbabwean women and girls from towns bordering South Africa, Mozambique, and Zambia are subjected to prostitution, sometimes being sold by their parents; Zimbabwean men, women, and children are subjected to forced labor in agriculture and domestic service in rural areas, as well as domestic servitude and sex trafficking in cities and towns; Zimbabwean women and men are lured into exploitative labor situations in Angola, Botswana, Mozambique, the United Arab Emirates, Malaysia, Nigeria, and South Africa with false job offers, while women and girls are lured to China, Egypt, the UK, and Canada and forced into prostitution; adults and children from Bangladesh, Somalia, India, Pakistan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia are trafficked through Zimbabwe en route to South Africatier rating: Tier 3 - Zimbabwe does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; tangible efforts to investigate and prosecute trafficking offenses, including those allegedly involving government officials, and to protect victims remain minimal; the government continues to rely on an international organization to provide law enforcement training and on NGOs to identify and assist victims without government support for such work; a national trafficking awareness campaign was launched in November 2012 (2013)Illicit drugs:transit point for cannabis and South Asian heroin, mandrax, and methamphetamines en route to South Africa"
Introduction ::ZimbabweBackground:The UK annexed Southern Rhodesia from the [British] South Africa Company in 1923. A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. In 1965 the government unilaterally declared its independence, but the UK did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country (then called Rhodesia). UN sanctions and a guerrilla uprising finally led to free elections in 1979 and independence (as Zimbabwe) in 1980. Robert MUGABE, the nation's first prime minister, has been the country's only ruler (as president since 1987) and has dominated the country's political system since independence. His chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. Ignoring international condemnation, MUGABE rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his reelection. In April 2005, the capital city of Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. President MUGABE in June 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months. General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with the opposition winning a majority of seats in parliament. MDC opposition leader Morgan TSVANGIRAI won the most votes in the presidential polls, but not enough to win outright. In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of TSVANGIRAI from the ballot. Extensive evidence of violence and intimidation resulted in international condemnation of the process. Difficult negotiations over a power-sharing government, in which MUGABE remained president and TSVANGIRAI became prime minister, were finally settled in February 2009, although the leaders failed to agree upon many key outstanding governmental issues. MUGABE was reelected president in June 2013 in balloting that was severely flawed and internationally condemned.Geography ::ZimbabweLocation:Southern Africa, between South Africa and ZambiaGeographic coordinates:20 00 S, 30 00 EArea:total: 390,757 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 61land: 386,847 sq kmwater: 3,910 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than MontanaLand boundaries:total: 3,066 kmborder countries: Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:tropical; moderated by altitude; rainy season (November to March)Terrain:mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld); mountains in eastElevation extremes:lowest point: junction of the Runde and Save Rivers 162 mhighest point: Inyangani 2,592 mNatural resources:coal, chromium ore, asbestos, gold, nickel, copper, iron ore, vanadium, lithium, tin, platinum group metalsLand use:arable land: 10.49%permanent crops: 0.31%other: 89.2% (2011)Irrigated land:1,735 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:20 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.21 cu km/yr (14%/7%/79%)per capita: 333.5 cu m/yr (2002)Natural hazards:recurring droughts; floods and severe storms are rareEnvironment - current issues:deforestation; soil erosion; land degradation; air and water pollution; the black rhinoceros herd - once the largest concentration of the species in the world - has been significantly reduced by poaching; poor mining practices have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollutionEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protectionsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural riverine boundary with Zambia; in full flood (February-April) the massive Victoria Falls on the river forms the world's largest curtain of falling water; Lake Kariba on the Zambia-Zimbabwe border forms the world's largest reservoir by volume (180 cu km; 43 cu mi)People and Society ::ZimbabweNationality:noun: Zimbabwean(s)adjective: ZimbabweanEthnic groups:African 98% (Shona 82%, Ndebele 14%, other 2%), mixed and Asian 1%, white less than 1%Languages:English (official), Shona, Sindebele (the language of the Ndebele, sometimes called Ndebele), numerous but minor tribal dialectsReligions:syncretic (part Christian, part indigenous beliefs) 50%, Christian 25%, indigenous beliefs 24%, Muslim and other 1%Population:13,182,908 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 72note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 39.4% (male 2,623,606/female 2,570,028)15-24 years: 22.5% (male 1,472,186/female 1,493,816)25-54 years: 30.8% (male 2,039,943/female 2,018,589)55-64 years: 3.7% (male 176,951/female 311,113)65 years and over: 3.6% (male 193,147/female 283,529) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 76.4 %youth dependency ratio: 69.6 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.8 %potential support ratio: 14.7 (2013)Median age:total: 19.5 yearsmale: 19 yearsfemale: 20 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:4.38% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Birth rate:32.41 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Death rate:11.4 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Net migration rate:22.76 migrant(s)/1,000 populationcountry comparison to the world: 3note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2013 est.)Urbanization:urban population: 38.6% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 3.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:HARARE (capital) 1.606 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.95 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.95 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.57 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.7 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:20.5note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011 est.)Maternal mortality rate:570 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 15Infant mortality rate:total: 27.25 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 71male: 29.63 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 24.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 53.86 yearscountry comparison to the world: 209male: 53.79 yearsfemale: 53.93 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:3.58 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 45Contraceptive prevalence rate:58.5% (2010/11)Physicians density:0.16 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:1.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 98% of populationrural: 69% of populationtotal: 80% of populationunimproved:urban: 2% of populationrural: 31% of populationtotal: 20% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 52% of populationrural: 32% of populationtotal: 40% of populationunimproved:urban: 48% of populationrural: 68% of populationtotal: 60% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:14.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1.2 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 9HIV/AIDS - deaths:83,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 143Children under the age of 5 years underweight:10.1% (2011)country comparison to the world: 68Education expenditures:2.5% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 158Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and write Englishtotal population: 83.6%male: 87.8%female: 80.1% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 9 yearsmale: 10 yearsfemale: 9 years (2003)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 7.6%country comparison to the world: 123male: 7.6%female: 7.6% (2004)Government ::ZimbabweCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Zimbabweconventional short form: Zimbabweformer: Southern Rhodesia, RhodesiaGovernment type:parliamentary democracyCapital:name: Hararegeographic coordinates: 17 49 S, 31 02 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:8 provinces and 2 cities* with provincial status; Bulawayo*, Harare*, Manicaland, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland East, Mashonaland West, Masvingo, Matabeleland North, Matabeleland South, MidlandsIndependence:18 April 1980 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 18 April (1980)Constitution:21 December 1979Legal system:mixed legal system of English common law, Roman-Dutch civil law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987); Vice President Joice MUJURU (since 6 December 2004) and Vice President John Landa NKOMO (since December 2009)head of government: Executive President Robert Gabriel MUGABE (since 31 December 1987) note - according to the new constitution, following the 31 July 2013 presidential elections the position of Prime Minister was abolishedcabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president; responsible to the House of Assembly(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: presidential candidates nominated with a nomination paper signed by at least 10 registered voters (at least one from each province) and elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); elections last held on 31 July 2013 (next to be held in 2018); co-vice presidents drawn from party leadershipelection results: Robert Gabriel MUGABE reelected president; percent of vote - Robert Gabriel MUGABE 61.1%, Morgan TSVANGIRAI 34.4%, Welshman NCUBE 2.7% other 1.8%; note - the election process was considered flawed and roundly criticised by election monitors and international bodiesLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of a Senate (93 seats - 60 members elected by popular vote for a five-year term, 10 provincial governors nominated by the president, 16 traditional chiefs elected by the Council of Chiefs, 2 seats held by the president and deputy president of the Council of Chiefs, and 5 members appointed by the president) and a House of Assembly (210 seats - members elected by popular vote for five-year terms)elections: last held on 31 July 2013 (next to be held in 2018)election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ZANU-PF 37 MDC 23; House of Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ZANU-PF 160, MDC 49, other 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 4 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president upon recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body consisting of the chief justice, Public Service Commission chairman, attorney general, and 2-3 members appointed by the president; judges normally serve until age 65, but can elect to serve until age 70subordinate courts: High Court, regional magistrate courts, and special courtsPolitical parties and leaders:African National Party or ANP [Egypt DZINEMUNHENZVA]Movement for Democratic Change - Tsvangirai or MDC-T [Morgan TSVANGIRAI]Movement for Democratic Change - Ncube or MDC-N [Welshman NCUBE]Peace Action is Freedom for All or PAFAUnited Parties [Abel MUZOREWA]United People's Party or UPP [Daniel SHUMBA]Zimbabwe African National Union-Ndonga or ZANU-Ndonga [Wilson KUMBULA]Zimbabwe African National Union-Patriotic Front or ZANU-PF [Robert Gabriel MUGABE]Zimbabwe African Peoples Union or ZAPU [Dumiso DABENGWA]Zimbabwe Youth in Alliance or ZIYAPolitical pressure groups and leaders:Crisis in Zimbabwe CoalitionNational Constitutional Assembly or NCA [Lovemore MADHUKU]Women of Zimbabwe Arise or WOZA [Jenny WILLIAMS]Zimbabwe Congress of Trade Unions or ZCTU [Wellington CHIBEBE]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Machivenyika MAPURANGAchancery: 1608 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 332-7100FAX: [1] (202) 483-9326Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador David Bruce WHARTONembassy: 172 Herbert Chitepo Avenue, Hararemailing address: P. O. Box 3340, Hararetelephone: [263] (4) 250-593 through 250-594FAX: [263] (4) 796-488, or 722-618Flag description:seven equal horizontal bands of green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow, and green with a white isosceles triangle edged in black with its base on the hoist side; a yellow Zimbabwe bird representing the long history of the country is superimposed on a red five-pointed star in the center of the triangle, which symbolizes peace; green represents agriculture, yellow mineral wealth, red the blood shed to achieve independence, and black stands for the native peopleNational symbol(s):Zimbabwe bird symbol; African fish eagleNational anthem:name: ""Kalibusiswe Ilizwe leZimbabwe"" [Northern Ndebele language] ""Simudzai Mureza WeZimbabwe"" [Shona] (Blessed Be the Land of Zimbabwe)lyrics/music: Solomon MUTSWAIRO/Fred Lecture CHANGUNDEGAnote: adopted 1994Economy ::ZimbabweEconomy - overview:Zimbabwe's economy is growing despite continuing political uncertainty. Following a decade of contraction from 1998 to 2008, Zimbabwe's economy recorded real growth of more than 9% per year in 2010-11, before slowing to 5% in 2012, due in part to a poor harvest and low diamond revenues. However, the government of Zimbabwe still faces a number of difficult economic problems, including infrastructure and regulatory deficiencies, ongoing indigenization pressure, policy uncertainty, a large external debt burden, and insufficient formal employment. Zimbabwe''s 1998-2002 involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government''s subsequent land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products. Until early 2009, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely printed money to fund the budget deficit, causing hyperinflation. Dollarization in early 2009 - which allowed currencies such as the Botswana pula, the South Africa rand, and the US dollar to be used locally - ended hyperinflation and reduced inflation to about 10%, but exposed structural weaknesses that continue to inhibit broad-based growth.GDP (purchasing power parity):$7.366 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 159$7.054 billion (2011 est.)$6.38 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$9.802 billionnote: in 2009, the Zimbabwean dollar was taken out of circulation, making Zimbabwe's GDP at the official exchange rate a highly inaccurate statistic (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7310.6% (2011 est.)9.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 227$500 (2011 est.)$500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 68%government consumption: 29.4%investment in fixed capital: 21.9%exports of goods and services: 67.9%imports of goods and services: -87.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 20.3%industry: 25.1%services: 54.6% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, cotton, tobacco, wheat, coffee, sugarcane, peanuts; sheep, goats, pigsIndustries:mining (coal, gold, platinum, copper, nickel, tin, diamonds, clay, numerous metallic and nonmetallic ores), steel; wood products, cement, chemicals, fertilizer, clothing and footwear, foodstuffs, beveragesIndustrial production growth rate:4.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Labor force:3.931 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 66%industry: 10%services: 24% (1996)Unemployment rate:95% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20280% (2005 est.)note: figures reflect underemployment; true unemployment is unknown and, under current economic conditions, unknowablePopulation below poverty line:68% (2004)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2%highest 10%: 40.4% (1995)Distribution of family income - Gini index:50.1 (2006)country comparison to the world: 2350.1 (1995)Budget:revenues: $NAexpenditures: $NATaxes and other revenues:NA% of GDPBudget surplus (+) or deficit (-):NA% of GDPPublic debt:187.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2180.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):8.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1845.4% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:7.17% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1975% (31 December 2007)Commercial bank prime lending rate:30% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 534% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$12.27 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 74$6.586 billion (31 December 2011 est.)note: Zimbabwe's central bank no longer publishes data on monetary aggregates, except for bank deposits, which amounted to $2.1 billion in November 2010; the Zimbabwe dollar stopped circulating in early 2009; since then, the US dollar and South African rand have been the most frequently used currencies; there are no reliable estimates of the amount of foreign currency circulating in ZimbabweStock of broad money:$11 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 104$22.71 billion (31 December 2012 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$9.844 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 99$6.289 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$10.9 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 70$11.48 billion (31 December 2010)$3.83 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:-$521.9 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 96-$621.5 million (2011 est.)Exports:$3.314 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127$2.932 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:platinum, cotton, tobacco, gold, ferroalloys, textiles/clothingExports - partners:China 20.4%, South Africa 14.9%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 12.9%, Botswana 11.5%, Italy 4.4% (2012)Imports:$4.569 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 132$4.272 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, other manufactures, chemicals, fuels, food productsImports - partners:South Africa 51.2%, China 9.7% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$575.6 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 147$660.3 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$8.767 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 102$6.276 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Zimbabwean dollars (ZWD) per US dollar -234.25 (2010)234.25 (2009)9,686.8 (2007)note: the dollar was adopted as a legal currency in 2009; since then the Zimbabwean dollar has experienced hyperinflation and is essentially worthlessEnergy ::ZimbabweElectricity - production:7.615 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Electricity - consumption:12.54 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Electricity - exports:53 million kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - imports:5.497 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.005 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Electricity - from fossil fuels:66.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:33.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Refined petroleum products - consumption:19,030 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Refined petroleum products - imports:13,140 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 124Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:8.493 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Communications ::ZimbabweTelephones - main lines in use:356,000 (2011)country comparison to the world: 109Telephones - mobile cellular:9.2 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 81Telephone system:general assessment: system was once one of the best in Africa, but now suffers from poor maintenancedomestic: consists of microwave radio relay links, open-wire lines, radiotelephone communication stations, fixed wireless local loop installations, and a substantial mobile-cellular network; Internet connection is available in Harare and planned for all major towns and for some of the smaller onesinternational: country code - 263; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat; 2 international digital gateway exchanges (in Harare and Gweru) (2010)Broadcast media:government owns all local radio and TV stations; foreign shortwave broadcasts and satellite TV are available to those who can afford antennas and receivers; in rural areas, access to TV broadcasts is extremely limited (2007)Internet country code:.zwInternet hosts:30,615 (2012)country comparison to the world: 108Internet users:1.423 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 84Transportation ::ZimbabweAirports:196 (2013)country comparison to the world: 29Airports - with paved runways:total: 17over 3,047 m: 32,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1791,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 104under 914 m:72 (2013)Pipelines:refined products 270 km (2013)Railways:total: 3,427 kmcountry comparison to the world: 50narrow gauge: 3,427 km 1.067-m gauge (313 km electrified) (2008)Roadways:total: 97,267 kmcountry comparison to the world: 45paved: 18,481 kmunpaved: 78,786 km (2002)Waterways:(some navigation possible on Lake Kariba) (2011)Ports and terminals:Binga, KaribaMilitary ::ZimbabweMilitary branches:Zimbabwe Defense Forces (ZDF): Zimbabwe National Army (ZNA), Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-24 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women are eligible to serve (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,616,051females age 16-49: 2,868,376 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,528,166females age 16-49: 1,646,041 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 154,870female: 152,550 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:3.8% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 26Transnational Issues ::ZimbabweDisputes - international:Namibia has supported, and in 2004 Zimbabwe dropped objections to, plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river; South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migrationRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: undetermined (political violence, human rights violations, land reform, and economic collapse) (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Zimbabwe is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Zimbabwean women and girls from towns bordering South Africa, Mozambique, and Zambia are subjected to prostitution, sometimes being sold by their parents; Zimbabwean men, women, and children are subjected to forced labor in agriculture and domestic service in rural areas, as well as domestic servitude and sex trafficking in cities and towns; Zimbabwean women and men are lured into exploitative labor situations in Angola, Botswana, Mozambique, the United Arab Emirates, Malaysia, Nigeria, and South Africa with false job offers, while women and girls are lured to China, Egypt, the UK, and Canada and forced into prostitution; adults and children from Bangladesh, Somalia, India, Pakistan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia are trafficked through Zimbabwe en route to South Africatier rating: Tier 3 - Zimbabwe does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; tangible efforts to investigate and prosecute trafficking offenses, including those allegedly involving government officials, and to protect victims remain minimal; the government continues to rely on an international organization to provide law enforcement training and on NGOs to identify and assist victims without government support for such work; a national trafficking awareness campaign was launched in November 2012 (2013)Illicit drugs:transit point for cannabis and South Asian heroin, mandrax, and methamphetamines en route to South Africa"
The World Factbook. 2014.
